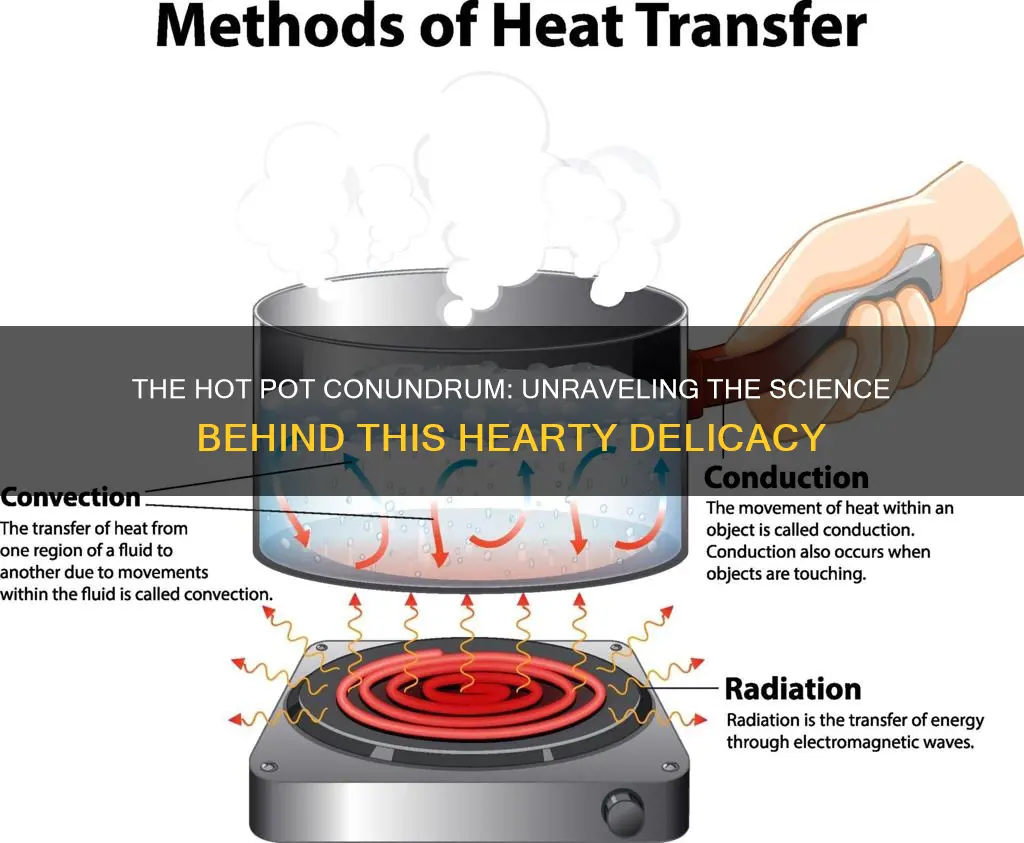
A hot pot transfers heat through a combination of conduction, convection, and radiation. When a pot is heated, the heat from the stove is transferred to the pot, which then heats the water inside through conduction. As the water heats up, it becomes less dense and rises to the top of the pot, while the colder, denser water sinks to the bottom. This movement of the fluid is convection. Radiation is also involved, as the stove emits electromagnetic waves that heat the pot without direct contact.
What You'll Learn

Convection vs. Conduction vs. Radiation
Heat transfer is the physical act of thermal energy being exchanged between two systems by dissipating heat. The three modes of heat transfer are conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction
Conduction is the direct transmission of heat energy between objects in direct contact. It is the most common form of heat transfer and occurs via physical contact. For example, placing your hand against a window or placing metal into an open flame. The slower-speed particles will increase in kinetic energy as a result of colliding with higher-speed particles. Conduction is a longer process than convection or radiation because it needs molecules to come into contact with one another.
Convection
Convection is the transfer of heat from one place to another made possible by the flow of fluids or liquids, and it happens in both liquids and gases. When a fluid, such as air or a liquid, is heated and then travels away from the source, it carries the thermal energy along. The fluid above a hot surface expands, becomes less dense, and rises. As the immediate hot air rises, it pushes denser, colder air down. This series of events represents how convection currents are formed. A space heater is a classic example of convection.
Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of energy using electromagnetic waves without involving particles. Thermal radiation is the direct result of random movements of atoms and molecules in matter. All materials radiate thermal energy based on their temperature. The sun is a clear example of heat radiation. At normal room temperatures, objects radiate as infrared waves. The temperature of the object affects the wavelength and frequency of the radiated waves. As temperature increases, the wavelengths within the spectra of the emitted radiation decrease and emit shorter wavelengths with higher-frequency radiation.
Choosing the Right Pan Connector
You may want to see also

Conduction transfers heat through contact
Conduction is the transfer of heat from one object to another through direct contact. It is one of the three primary methods of heat transfer, the other two being convection and radiation.
When you place a pot on a stove, the heat from the stove is transferred to the pot, which in turn heats up the water inside. This is an example of conduction, as the heat is transferred from the stove to the pot at the points where the two are in direct contact. The heat is then conducted from the pot to the water.
The efficiency of this heat transfer depends on the conductivity of the materials involved. For instance, copper is an excellent conductor of heat, allowing heat to move through cookware and be transferred to food quickly. On the other hand, water and stainless steel are relatively poor conductors of heat. This is why food continues to cook even after being removed from the heat source.
In the context of cooking, conduction is a static process compared to convection, which involves the movement of fluids, such as the stirring of soup or the motion of boiling water. Convection ovens utilise this principle by incorporating a fan that blows hot air around, resulting in faster and more even cooking compared to conventional ovens.
It is important to note that multiple heat transfer methods can occur simultaneously. For example, when using a gas burner, heat is transferred primarily through convection, with smaller contributions from conduction and radiation. Similarly, when using a ceramic cooking surface, heat transfer occurs mainly through conduction, but radiation and convection also play a role due to the imperfect contact between the pot and the surface.
Induction cooking is a unique method that does not rely on direct radiation, convection, or thermal conduction. It uses electromagnetic induction to create eddy currents in the ferrous metal base of the cookware, resulting in resistive heating. This technology allows for rapid increases in temperature and efficient heat transfer, making it a popular choice for modern kitchens.
Simmering Hot Chocolate: The Slow Cooker's Sweet Secret
You may want to see also

Convection uses the movement of fluids
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids, both liquids and gases. It is one of the three methods of heat transfer, the other two being conduction and radiation.
Convection is a more efficient method of heat transfer than conduction because it adds the element of motion. A convection oven, for example, heats food faster than a conventional oven because it has a fan that blows hot air around. Convection ovens can reduce cooking times by 25% or more compared with ordinary ovens. They also tend to increase the browning of food by concentrating more heat on the food's outer surface.
The movement of steam or the motion of boiling water in a pot are examples of convection. Stirring a pot of soup is also a form of convection, as it redistributes the heat from the bottom of the pot throughout the soup.
Convection is also the reason that frozen items thaw more quickly under cold running water than if they are simply submerged in water. When a pot of water is placed on a stove to boil, conduction heat warms up the pot, which then heats the water molecules inside. As these molecules heat up, convection causes them to move away from the interior of the pot as they are replaced by cooler molecules. This continuous current creates convection heat transfer within the water.
Convection also plays a role in heating a house during the winter. In cold climates, vents are usually located on the floor. These vents release heat into the house, warming the air at floor level. The hot air rises, making the cooler air sink, where it then becomes heated. This cycle continues, warming all of the air in the house.
Upflow Furnace: Drain Pan Needed?
You may want to see also

Radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves
Heat transfer is an exchange of thermal energy between two objects. There are three methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. While conduction and convection require direct or indirect contact between the two objects, radiation does not. Radiation is the transfer of heat energy through space by electromagnetic radiation.
Radiation heat transfer is a process where heat waves are emitted and may be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted through a colder body. Radiation heat transfer occurs in solids, liquids, and gases. It can also occur between two bodies separated by a colder medium.
Radiation heat transfer becomes important at high temperatures (above 1000 Kelvin) and when structures are in direct view of hot debris located below. The rate of radiation heat transfer is determined by the view factor, which is the configuration of the bodies involved. The higher the temperature of a body, the greater the amount of energy radiated.
The sun generates energy, which is transferred through space to the Earth's atmosphere and surface. Most of the electromagnetic radiation that comes to Earth from the sun is in the form of visible light. Our brains interpret different frequencies of this light as colors, including red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. When the eye views all these colors at the same time, it is interpreted as white. Waves from the sun that we cannot see include infrared, which has a lower frequency than red light, and ultraviolet, which has a higher frequency than violet light.
In cooking, radiation is the process where heat and light waves strike and penetrate food. There is no direct contact between the heat source and the food. Examples of cooking with radiation include warming your hands over a fire, lying in the sun to get warm, and heating up food in the microwave.
Roasting a Whole Chicken in a Cast Iron Pan: A Beginner's Guide
You may want to see also

Convection is a more efficient method of heat transfer
When cooking, it is important to understand the process of heat transfer to ensure food is cooked efficiently and safely. There are three methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. While conduction is the most common type of heat transfer, convection is a more efficient method because it adds the element of motion.
Conduction is the process of heat being transferred between objects through direct contact. For example, when cooking with a stove, the burners conduct heat energy to the bottom of a pan sitting on top of it. The pan then conducts heat to its contents. Conduction is the slowest method of heat transfer, but it allows for food to be cooked from the outside in.
Convection, on the other hand, combines conduction heat transfer with circulation to force molecules in the air to move from warmer areas to cooler ones. As the molecules closest to the heat source become warm, they rise and are replaced by cooler molecules. This creates a circulating current that evenly distributes heat. For example, when a pot of water is placed on a stove, conduction heat warms up the pot, which then heats the water molecules inside. As these molecules heat up, convection causes them to move away from the interior of the pot as they are replaced by cooler molecules. This continuous current creates convection heat transfer within the water.
The movement of steam or the motion of boiling water in a pot are further examples of convection. Stirring a pot of soup is also considered a form of convection, as it redistributes the heat from the bottom of the pot throughout the soup. Additionally, convection is the reason that frozen items thaw more quickly under cold running water than if they are simply submerged in water.
In summary, while conduction is the most basic and common method of heat transfer in cooking, convection is a more efficient method due to its incorporation of motion. Convection ovens, the movement of steam and boiling water, and the stirring of soup are all examples of how convection can efficiently distribute heat during the cooking process.
The Perfect Sear: Timing Your Steak
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A hot pot involves all three types of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs when the pot comes into direct contact with the heat source, such as a stove, and the heat is transferred to the pot. Convection takes place when the water in the pot is heated, causing the warmer water to rise and the cooler water to sink, creating a convection current. Radiation is observed when the heat from the stove or the pot can be felt without touching it, as the heat is transferred through electromagnetic waves.
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects. Convection involves the movement of fluids, such as liquids or gases, to transfer heat. Radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves, and it does not require a medium or direct contact to transfer heat.
Conduction occurs when a stove heats up a pan, and the heat is then transferred to the food inside the pan. Convection can be observed when boiling water, as the heated water at the bottom rises, while the cooler water sinks, creating a convection current. Radiation is evident when you can feel the heat from a stove or a fire without touching it, as the heat is radiated through electromagnetic waves.







