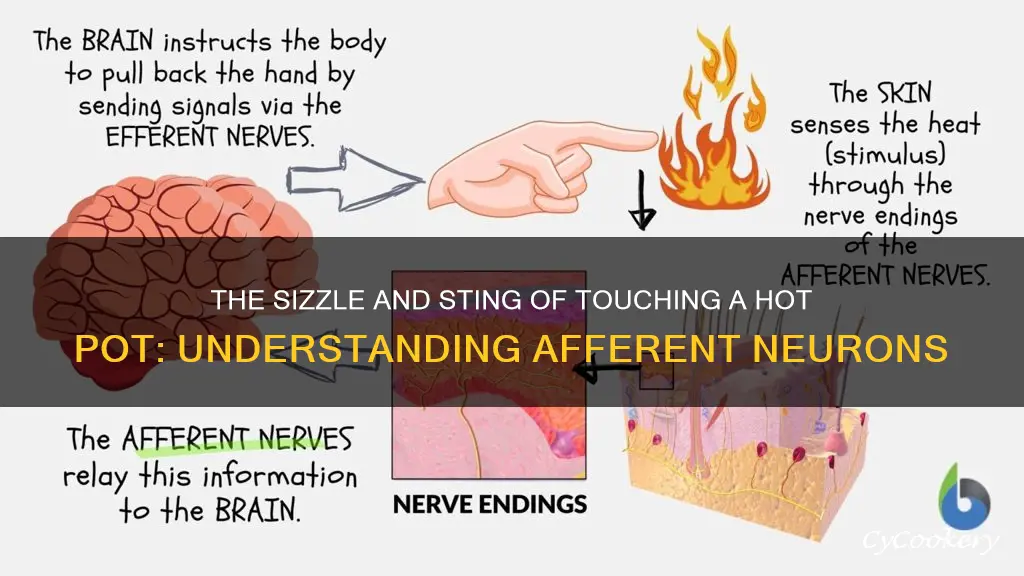
Touching a hot pot is a perfect example of a reflex action. This automatic response is made possible by afferent neurons, which are sensory neurons that transmit information from the skin to the central nervous system (CNS). In this case, the afferent neurons detect the high temperature and send electrical nerve impulses to the spinal cord. This triggers a motor response, prompting the arm muscles to contract and pull the hand away from the hot pot. This rapid process occurs before the brain has time to process the threat, demonstrating the crucial role of afferent neurons in protecting us from harm.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type of neuron | Afferent |
| Type of nerve pathway | Afferent |
| Direction of information | Towards the central nervous system |
| Type of impulse | Sensory |
| Type of neuron structure | Long dendron, short axon |
| Shape of cell body | Round and smooth |
| Location of cell body | Outside the central nervous system |
| Function | Transfer signals or messages from different organs and tissues to the brain or spinal cord |
| Location of afferent cells | Ears, tongue, skin |
What You'll Learn

Afferent neurons are sensory neurons
When you touch a hot pot, your skin receptors quickly send nerve impulses to the spinal cord via afferent neurons. These neurons are activated by the stimulus of the hot pot and send a signal to the CNS. In this case, the afferent neurons carry sensory information from your hand to your brain, letting it know your body is touching something hot.
The cell body of an afferent neuron is located outside the CNS, in the dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord. Its distinctive design features one axon that splits into two branches: one connected to the sensory organ and the other responsible for transferring data from the sensory systems to the spinal cord through dorsal roots.
Afferent neurons are often associated with sensory or input function, gathering information from sensory perceptions such as light, smell, taste, hearing, touch, and pain. They are crucial for our conscious perception of the environment and our responses to it.
In summary, afferent neurons are sensory neurons that transmit information from sensory receptors in the skin and organs to the CNS. They play a vital role in detecting and responding to different stimuli, ensuring our survival and protection from harm.
Pizza Hut's Pan Pizza: Detroit-Style?
You may want to see also

They carry nerve impulses from sensory stimuli to the central nervous system
Afferent neurons are a type of sensory neuron that carry nerve impulses from sensory stimuli to the central nervous system. They are a crucial component of the body's reflex system, facilitating our survival by triggering quick withdrawal from harmful stimuli.
When you accidentally touch a hot pot, your skin receptors, or thermoreceptors, detect the change in temperature and quickly send electrical nerve impulses to the spinal cord via afferent neurons. These neurons convert the external stimuli into internal electrical impulses, carrying the signal through their nerve fibres to the central nervous system.
The afferent neurons are responsible for transmitting the sensory information from the skin receptors to the spinal cord, where interneurons, or relay neurons, process the impulses and coordinate a response. The interneurons connect the afferent sensory neurons with the correct motor neurons, which then stimulate the muscles to contract, causing you to pull your hand away from the hot pot.
This entire process, from the initial sensory stimulus to the motor response, occurs very rapidly, often before the message reaches the brain. This results in a quick reaction time as the thinking process of the brain can be relatively slow in comparison.
Afferent neurons play a vital role in detecting and responding to various sensory stimuli, including light, smell, touch, taste, and hearing. They are essential for our survival, enabling us to react to potentially harmful situations and protect ourselves from injury.
Gold Pan Size: Choosing the Right Fit
You may want to see also

Afferent neurons are located outside the central nervous system
Afferent neurons are a type of sensory neuron that carries information from the body's sensory receptors to the central nervous system (CNS). They are also known as 'sensory neurons' or 'afferent sensory' neurons.
When you touch a hot pot, your skin receptors send electrical nerve impulses via afferent neurons to the spinal cord (CNS). Afferent neurons are located outside the CNS, with their cell bodies in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. In the spinal cord, the impulses are processed, and a response is sent back via motor neurons, prompting you to pull your hand away from the hot pot. This response is a 'reflex action'.
Afferent neurons have a distinctive structure, with a smooth and rounded cell body and a single process leaving the cell body, dividing into two branches. One branch is long and reaches towards the sensory organ, and the other is short and extends towards the CNS.
Afferent neurons are essential for transmitting sensory data, such as touch, temperature, pain, vibrations, and even potentially damaging signals, to the CNS. They are located in various organs and body parts, including the tongue, ears, skin, nose, airways, urinary tract, and cardiac muscle.
Stainless Steel Pans: Why the White Film?
You may want to see also

They convert external stimuli into internal electrical impulses
Afferent neurons are nerve fibres that convert external stimuli into internal electrical impulses. They are also known as sensory neurons and are responsible for transmitting sensory information from the outside world to the brain.
When you touch a hot pot, your afferent neurons are activated. The heat is sensed by a receptor in your fingers, which triggers an impulse in a neuron. This neuron then transmits the message to the central nervous system (CNS), specifically the spinal cord. The impulse travels to the CNS via the dorsal root, which contains afferent nerve fibres. In the spinal cord, the impulse is processed, and a response is formulated.
The afferent neurons in this scenario are converting the external stimulus of touching a hot pot into an internal electrical impulse that travels to the CNS. This impulse carries the information that the body is touching something hot.
Once the CNS receives the impulse, it coordinates a response via efferent signals. Efferent neurons, or motor neurons, carry these signals from the CNS to the muscles, instructing them to contract and move your hand away from the hot pot. This response occurs very quickly, often before the message reaches the brain, as the process of thinking and deciding on a course of action can be time-consuming.
Afferent neurons play a crucial role in our survival by allowing us to react to potentially harmful stimuli in our environment. They are responsible for detecting and transmitting a wide range of sensory information, including touch, temperature, pain, taste, and more.
Scrap Metal Disposal: Pots and Pans
You may want to see also

Afferent neurons have long dendrites and a short axon
Touching a hot pot triggers a reflex action, a response that occurs before the brain gets the time it needs to process the threat. At the point of contact, skin receptors send nerve impulses to the spinal cord via sensory neurons. These sensory neurons are also known as afferent neurons.
The afferent neuron plays a crucial role in converting external stimuli, such as touch and temperature, into internal electrical impulses. These nerve impulses are then carried through the nerve fibers of the afferent neuron to the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. The cell body of the afferent neuron is located in the dorsal ganglia of the spinal cord, positioning it to receive and transmit sensory information efficiently.
In summary, the structure of afferent neurons, with their long dendrites and short axon, is specifically designed to facilitate the reception and rapid transmission of sensory information, such as the sensation of touching a hot pot. This structural design ensures an efficient and quick response to external stimuli, contributing to our survival and well-being.
Chrome Racks: Scratch-Free Solution for Pots and Pans
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Afferent neurons are sensory neurons that carry nerve impulses from sensory stimuli towards the central nervous system and brain.
Afferent neurons carry sensory information from your hand to your brain, letting it know your body is touching something hot.
The brain then processes this information and uses efferent neurons to tell the arm muscle to contract and move your hand away.
Afferent neurons carry signals from the body to the brain, while efferent neurons carry signals from the brain to the body.
This process is called a 'reflex action'.







