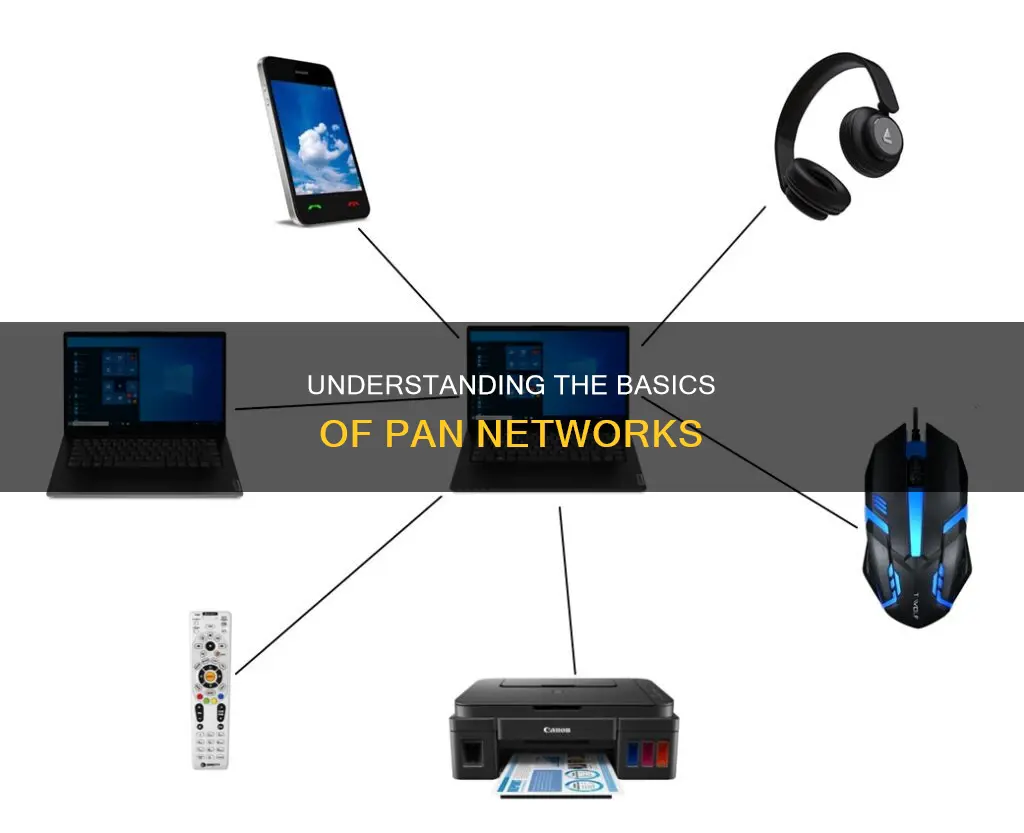
A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network that connects electronic devices within a user's immediate area. The size of a PAN ranges from a few centimetres to a few metres. PANs can be used for communication between devices or for connecting to a higher-level network and the internet, with one master device serving as the gateway. PANs typically consist of laptops, smartphones, tablets, wearables, personal digital assistants, printers and entertainment devices. PANs don't include a router so they can't connect to the internet directly, but the devices in a PAN are generally interconnected using some form of wireless technology.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Range | A few centimeters to several meters |
| Connection type | Wired or wireless |
| Wired connection methods | USB, FireWire, IEEE-1394, Thunderbolt |
| Wireless connection methods | Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, IrDA, Zigbee, UWB |
| Devices connected | Computers, smartphones, tablets, printers, keyboards, wireless mouse, wireless headphones, smartwatches, etc. |
| Use cases | Home, offices, small network areas, healthcare, schools, military, etc. |
| Advantages | Flexibility, efficiency, easy setup, low cost, portability, reliability, easy data synchronization, lower power consumption |
| Disadvantages | Short network range, slow data transfer, no broadcasting option, signal interference, cost, line of sight propagation, less reliable |
What You'll Learn

Wireless PAN
A Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) is a group of devices connected without the use of wires or cables. WPANs are designed to serve a single person in a small office or home office (SOHO) environment. They are carried over a low-powered, short-distance wireless network technology, with a range of just a few meters. WPANs use wireless connectivity protocols such as Bluetooth, Zigbee, Wireless USB, NearLink, and Infrared Data Association (IrDA) protocol devices.
WPANs are ideal for connecting devices in the immediate vicinity of a user and their workspace. They are commonly used to connect devices such as laptops, smartphones, tablets, printers, keyboards, and other computerized devices. WPANs are also used for body area networks (BANs), which involve medical sensors with wireless connectivity placed on or near the human body, such as pacemakers.
Bluetooth is the most common wireless connectivity protocol for WPANs. A Bluetooth WPAN, also called a piconet, is composed of up to 8 active devices in a master-slave relationship, with the first Bluetooth device in the network acting as the master. A piconet typically has a range of 10 meters, but can reach up to 100 meters under ideal circumstances. Bluetooth mesh networking extends the range and number of devices by using mesh networking techniques to relay information.
WPANs offer several advantages, including flexibility, efficiency, ease of setup, portability, and lower power consumption. However, they also have some disadvantages, such as limited network range, slow data transfer rates, signal interference, and higher costs for built-in WPAN devices.
Replacing Oil Pan on Gy6 50cc: Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Wired PAN
A personal area network (PAN) is a small network that interconnects technology devices within a limited range of just a few meters. This type of network is designed to enable devices in a small office or home office (SOHO) environment to communicate and share resources, data, and applications either wired or wirelessly.
While wireless communication is more common in PANs, a PAN can be wired as well. Wired PANs provide short connections between peripherals using wired technologies, such as USB, FireWire, IEEE-1394 high-performance serial buses, or a Thunderbolt hardware interface.
In addition, wired PANs can provide a more secure and reliable connection compared to wireless PANs, as they are less susceptible to interference from other wireless signals or devices. This can be especially important for sensitive data or information that needs to be protected.
Oil Pan Maintenance: Preventing the Gunk and Grime
You may want to see also

Body Area Network
A body area network (BAN), also known as a wireless body area network (WBAN), a body sensor network (BSN), or a medical body area network (MBAN), is a wireless network of wearable computing devices. These devices may be embedded inside the body as implants or pills, surface-mounted on the body, or carried in different positions, such as in pockets, by hand, or in bags. BANs are considered a type of personal area network (PAN) or wireless personal area network (WPAN).
BAN devices are becoming smaller and typically include multiple small body sensor units (BSUs) and a single central unit (BCU). Despite this trend, larger smart devices, such as tablets, still play an important role in BANs by acting as data hubs, gateways, and user interfaces for managing BAN applications.
The development of WBAN technology began around 1995 with the idea of using WPAN technologies to enable communication on, near, and around the human body. The term "BAN" was introduced around 2001 to refer specifically to systems where communication occurs entirely within, on, and in the immediate proximity of a human body.
WBAN systems can use WPAN wireless technologies as gateways to reach longer ranges and connect to the internet. This allows medical professionals to access patient data online, regardless of the patient's location, enabling remote health monitoring and telemedicine.
BANs have a wide range of applications, including:
- Health and wellness monitoring: BANs can be used to monitor vital signs, detect falls, and track physiological changes to monitor a patient's health status.
- Sports and leisure: BANs can be used to measure performance and improve training routines.
- Personalized medicine: BANs can include heart monitors, insulin pumps, and other personalized medical devices.
- Military and security: BANs can assist with seamless exchanges of information between individuals or between individuals and machines.
The Crock-Pot Conundrum: Hot Enough to Kill Bacteria?
You may want to see also

Offline Network
An offline network is a type of personal area network (PAN) that connects multiple devices through Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. This type of network is typically established in a home office environment, where devices such as printers, TVs, game systems, laptops, and other home appliances are integrated without using the internet.
The main advantage of an offline network is its ease of setup and relatively low cost. It requires no complex installation or cable connections, making it more cost-effective than traditional networks. Additionally, an offline network provides flexibility and high efficiency for short network ranges.
However, it is important to note that an offline network has limited data transfer rates due to the use of technologies like Bluetooth, which cannot handle large volumes of data at high speeds. This results in slower data transfer rates compared to other networks such as WAN, LAN, and MAN.
Another disadvantage of an offline network is its limited network coverage area or range. The network can transmit data within a range of about 10 meters, and the number of connected devices is also restricted.
In summary, an offline network is a convenient and cost-effective way to connect multiple devices in a small, single-space network without an internet connection. However, it has limitations in terms of data transfer rates and network coverage.
Moisture Pan GQF 1502: Water Level Check
You may want to see also

Home Office
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is a network that connects devices within a person's immediate vicinity, typically within a range of 10 meters. PANs are commonly used in home offices, where a separate, smaller network is set up for work purposes, distinct from the network used by other home appliances. This allows for the sharing of resources, data, and applications between devices, and can be done through wired or wireless connections.
In a home office setting, a PAN can be used to connect devices such as computers, laptops, printers, smartphones, tablets, and other entertainment devices like speakers and video game consoles. This enables easy data synchronization and sharing of resources between different devices. For example, a laptop can be connected to a printer to print documents or to a smartphone to transfer files. PANs also provide flexibility and efficiency, especially in a home office environment, due to their ease of setup and relatively low cost.
However, it is important to note that PANs have limited network coverage and are restricted to relatively low data rates. Additionally, devices within a PAN may not be compatible with each other, and the built-in WPAN devices can be costly.
Greasing the Pan: To Do or Not to Do?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is a computer network that connects devices within a person's immediate vicinity, typically within a range of 10 meters. PANs can be wireless or wired and are commonly used in homes, offices, and small network areas.
A PAN typically connects devices such as computers, smartphones, tablets, printers, personal digital assistants (PDAs), keyboards, mice, and other entertainment devices like speakers and video game consoles.
A PAN can work through wireless connections, such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, or Infrared Data Association (IrDA), or wired connections like USB, FireWire, or Thunderbolt. These connections enable data sharing and communication between the connected devices.
PANs offer flexibility, efficiency, ease of setup, portability, and lower costs compared to traditional networks. They also provide stable and reliable connections within a limited range.
PANs have limited network coverage, slower data transfer rates, compatibility issues, and can interfere with radio signals. Additionally, built-in wireless PAN devices can be costly, and the network range may pose security concerns due to the close proximity of devices.







